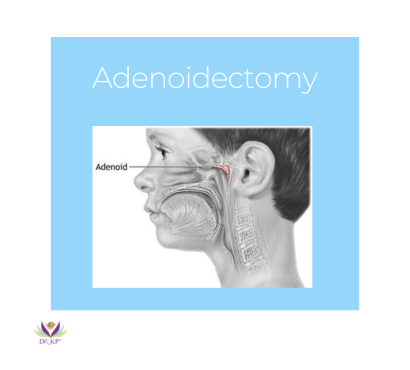
Adenoids are small lymphatic tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity that play a crucial role in a child’s immune system. However, enlarged adenoids can cause breathing difficulties, sleep disturbances, ear infections, and chronic nasal congestion. When these issues become persistent, an adenoidectomy—a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids—can provide long-term relief.
In this blog, we’ll discuss:
✔ What adenoids are and their function
✔ Common causes of enlarged adenoids
✔ Symptoms and when to seek medical help
✔ Adenoidectomy procedure, recovery, and benefits
What Are Adenoids?
Adenoids are part of the immune system, located behind the nose and above the throat. They help trap bacteria and viruses, preventing infections in young children. Unlike tonsils, which are visible in the throat, adenoids are hidden behind the nasal passages.
As a child grows, adenoids usually shrink and disappear by adolescence. However, in some cases, they remain enlarged and cause chronic breathing and ear problems.
Causes of Enlarged Adenoids
Several factors contribute to adenoid hypertrophy (enlarged adenoids):
✔ Frequent Infections – Recurrent bacterial or viral infections can cause chronic adenoid swelling.
✔ Allergies – Dust, pollen, and pet dander can lead to inflammation of adenoid tissue.
✔ Genetic Factors – Some children naturally have larger adenoids than others.
✔ Chronic Sinusitis – Prolonged sinus infections can contribute to adenoid enlargement.
✔ Exposure to Irritants – Pollution, cigarette smoke, and dust can worsen adenoid swelling.
Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoids
Children with enlarged adenoids may experience:
✔ Nasal congestion (stuffy or blocked nose)
✔ Mouth breathing (instead of breathing through the nose)
✔ Snoring and sleep apnea (gasping or pauses in breathing while sleeping)
✔ Frequent ear infections (due to blocked Eustachian tubes)
✔ Runny nose and postnasal drip
✔ Muffled hearing or speech issues
✔ Difficulty swallowing or a nasal voice
If your child experiences these symptoms frequently, consult an specialist to evaluate whether adenoidectomy is needed.
When is Adenoidectomy Necessary?
A doctor may recommend adenoid removal surgery if:
✔ The child has chronic breathing issues due to severely enlarged adenoids.
✔ There are recurring ear infections that affect hearing.
✔ The child snores loudly and has difficulty sleeping.
✔ Medications such as antibiotics and steroids fail to provide relief.
Adenoidectomy is a safe and effective solution, offering long-term relief from infections and breathing problems.
Adenoidectomy: The Surgical Procedure
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Before the procedure, the doctor will:
✔ Perform a nasal endoscopy or imaging tests.
✔ Check for allergies or bleeding disorders.
✔ Advise fasting for 6-8 hours before surgery.
How is Adenoidectomy Performed?
1️⃣ Anesthesia – The procedure is done under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is asleep and pain-free.
2️⃣ Surgical Removal – The surgeon removes the adenoids through the mouth using a curette (scraping tool), laser, or suction device.
3️⃣ Bleeding Control – A cautery device is used to stop bleeding.
4️⃣ No External Incision – The entire procedure is performed through the mouth, leaving no visible scars.
Duration
⏳ The surgery typically takes 15-30 minutes. Most patients are discharged the same day.
Recovery After Adenoidectomy
Post-Surgery Care
✔ Mild throat pain and nasal congestion are common for a few days.
✔ Encourage soft foods like soups, yogurt, and mashed potatoes.
✔ Hydration is crucial—plenty of fluids help with healing.
✔ Avoid spicy, hard, or acidic foods that may irritate the throat.
✔ Rest for at least a week, avoiding strenuous activities.
Expected Recovery Time
⏳ Most children recover within 1-2 weeks with minimal discomfort. Full benefits—improved breathing, reduced infections, and better sleep—can be seen within a month.
Benefits of Adenoidectomy
✔ Better breathing – No more nasal congestion or mouth breathing.
✔ Improved sleep – Reduces snoring and sleep apnea.
✔ Fewer ear infections – Lowers the risk of chronic ear problems.
✔ Less throat and sinus infections – Enhances overall respiratory health.
✔ Better quality of life – Increased energy, focus, and well-being.
Risks and Complications
Adenoidectomy is generally safe, but like any surgery, it carries some risks:
✔ Mild bleeding – Rare but can happen during or after surgery.
✔ Temporary throat discomfort – Lasts a few days.
✔ Nasal regurgitation – Rare, but some children may experience liquid coming out of the nose while swallowing.
Consult your doctor if your child has persistent fever, severe pain, or bleeding after surgery.
Adenoidectomy is a safe and effective solution for children suffering from enlarged adenoids, breathing difficulties, and recurrent infections. By removing the adenoids, the child experiences better sleep, fewer infections, and improved quality of life. If your child has persistent nasal congestion, snoring, or ear problems, consult an specialist to discuss whether adenoidectomy is the right option.
FAQs
1. At what age is adenoidectomy recommended?
Adenoidectomy is typically recommended for children between 2-10 years old if they have severe breathing, sleeping, or ear-related issues.
2. Can adenoids grow back after surgery?
In rare cases, adenoids can regrow, but this happens in only a small percentage of children. If symptoms persist, a re-evaluation is needed.
3. Is adenoidectomy painful?
No, the procedure is painless as it is performed under general anesthesia. After surgery, mild throat discomfort may last a few days but improves with medication.